以高濃度血小板血清治療內因性括約肌缺損之應力性尿失禁-何種病人可以得到好處?
李秉叡、江元宏、郭漢崇
佛教慈濟醫療財團法人花蓮慈濟醫院 泌尿部
Therapeutic efficacy of platelet-rich plasma in treatment of stress urinary incontinence due to intrinsic sphincter deficiency- which patients may benefit?
Ping-Jui Lee, Yuan-Hong Jiang, Hann-Chorng Kuo
Department of Urology, Hualien Tzu Chi Hospital, Buddhist Tzu Chi Medical Foundation and Tzu Chi University, Hualien, Taiwan
Purpose: Autologous platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is rich of cytokines and growth factors. The wide range of secreted proteins and growth factors within the α-granules promotes thrombosis and hemostasis, as well as chemotaxis, cellular proliferation, differentiation, angiogenesis, vascular modeling, and immune interactions. PRP emerged as the most innovative formulation in the treatment of osteoarthritis, chondral pathologies, non-union fractures, tendinopathies, muscle strains, and neuropathies. Intrinsic sphincter deficiency (ISD) is an important cause of stress urinary incontinence (SUI). The aim of this study is to investigate the clinical therapeutics of PRP treatment in ISD.
Materials and Methods: This prospective, single-center study was performed in Hualien Tzu Chi Hospital (Hualien, Taiwan), and approved by the Institutional Review Board and Ethics Committee of the hospital. Patients were informed about the study rationale and procedures; written informed consent was provided by all patients prior to enrollment and treatment. The population recruited in this study comprised patients with SUI due to ISD who showed limited recovery of urinary continence who were refractory to conventional treatments or failure after surgical therapy. Patients received 4 monthly urethral sphincter injection of 5mL PRP (extracted from 50ml of their own whole blood). Global response assessment ≥ 2 and ≥ 1 were defined as success and improvement, respectively. Evaluation of urinary incontinence severity with visual analog scale (VAS, from 0-10, from continence to total incontinence) and VUDS were done at baseline and 3 months after the last treatment. We performed subgroup analysis based on the etiology of urinary incontinence (neurogenic vs non-neurogenic) as we hypothesized that there may be differences in treatment effect based on this characteristic.
Results: Totally 31 non-neurogenic (26 post-prostatectomy incontinence male patients) and 4 neurogenic SUI patients with a mean age of 68.7±12.0 were enrolled. In overall patients, the postoperative GRA was 1.46±0.95, the improve rate was 85.7% (50.0% and 90.3% in neurogenic, and non-neurogenic SUI, respectively, p=0.089), and the success rate was 51.4% (0% and 58.1% in neurogenic, and non-neurogenic SUI, respectively, p=0.045) (Table 1). Among VUDS parameters, the changes of voided volume and abdominal leak point pressure were significantly difference between neurogenic and non-neurogenic SUI group. After PRP treatment, urinary incontinence severity by VAS significantly improved from 6.6±1.9 to 3.9±2.2 (mean difference: −2.73; 95% confidence interval: −3.40 to −2.08; P < 0.001) (Table 2). Urinary incontinence significantly improved soon after each urethral PRP treatment and was exclusively in non-neurogenic SUI group (Table 2). Perioperatively, there was no occurrence of adverse events or severe complications. Only 2 patients had urinary tract infection episodes after injection.
Conclusions: Injection of PRP in the urethral sphincter is a safe and effective treatment, providing marked reduction in the severity of SUI for patients. Non-neurogenic SUI patients (especially male PPI patients) seemed to have more benefits than neurogenic ones.
Table 1. Demographics and the treatment outcomes in ISD with SUI patients after PRP injection treatment
|
|
Neurogenic SUI
N=4
|
Non-neurogenic SUI
N=31
|
Total
|
P-value
|
|
|
Demographic
|
|||||
|
Age
|
46.5±11.90
|
71.55±8.63
|
68.69±11.98
|
<0.001
|
|
|
Gender
|
3M, 1F
|
27M, 4F
|
30M, 5F
|
0.477
|
|
|
Postoperative outcomes
|
|||||
|
GRA
|
0.50±0.58
|
1.58±0.92
|
1.46±0.95
|
0.030
|
|
|
Improvement rate
|
50.0%
|
90.3%
|
85.7%
|
0.089
|
|
|
Success rate
|
0.00%
|
58.1%
|
51.4%
|
0.045
|
|
|
VUDS parameters
|
|||||
|
CBC(mL)
|
Baseline
|
178.25±195.88
|
310.78±134.99
|
288.00±144.83
|
|
|
After treatment
|
205.00±248.35
|
346.74±194.04
|
325.74±203.98
|
|
|
|
Δ
|
26.75±57.86
|
35.96±218.61
|
34.59±202.08
|
0.935
|
|
|
Pdet (cmH2O)
|
Baseline
|
11.50±23.00
|
14.86±11.09
|
13.73±11.89
|
|
|
After treatment
|
0.00±0.00
|
16.00±11.71
|
13.44±12.26
|
|
|
|
Δ
|
-11.50±23.00
|
1.14±12.29
|
-0.88±14.64
|
0.115
|
|
|
Qmax (mL/s)
|
Baseline
|
8.50±9.95
|
9.91±5.24
|
9.41±5.69
|
|
|
After treatment
|
3.25±4.72
|
12.43±5.39
|
11.07±6.18
|
|
|
|
Δ
|
-5.25±6.18
|
2.52±7.08
|
1.37±7.39
|
0.079
|
|
|
cQmax
|
Baseline
|
0.6622±0.6720
|
0.5866±0.2723
|
0.5703±0.3305
|
|
|
After treatment
|
0.1536±0.2106
|
0.6943±0.2262
|
0.6142±0.2945
|
|
|
|
Δ
|
-0.5086±0.6539
|
0.1077±0.3245
|
0.0164±0.4338
|
0.155
|
|
|
Vol (mL)
|
Baseline
|
128.25±197.66
|
243.74±127.23
|
226.18±141.79
|
|
|
After treatment
|
105.00±198.18
|
292.39±156.66
|
264.63±172.92
|
|
|
|
Δ
|
-23.25±17.73
|
48.65±160.71
|
38.00±150.23
|
0.049
|
|
|
PVR (mL)
|
Baseline
|
125.00±150.00
|
69.22±114.04
|
72.12±113.09
|
|
|
After treatment
|
175.00±150.00
|
54.35±188.24
|
72.22±185.71
|
|
|
|
Δ
|
50.00±57.74
|
-14.87±187.53
|
-5.26±175.20
|
0.505
|
|
|
AG number
|
Baseline
|
-25.00±26.87
|
-3.32±12.06
|
-4.46±15.35
|
|
|
After treatment
|
-13.00±9.90
|
-7.84±14.78
|
-8.33±14.28
|
|
|
|
Δ
|
12.00±16.97
|
-4.53±18.81
|
-2.95±18.91
|
0.250
|
|
|
ALPP § (cmH2O)
|
Baseline
|
95.67±108.58
|
83.73±41.73
|
85.72±53.31
|
|
|
After treatment
|
57.67±51.54
|
105.58±47.01
|
96.00±50.09
|
|
|
|
Δ
|
-38.00±60.69
|
32.58±33.71
|
18.47±47.68
|
0.015
|
|
Abbreviation:
AB number: Abrams–Griffiths number; ALPP: abdominal leak point pressure; CBC: cystometric bladder capacity; cQmax: corrected maximum flow rate; Pdet: detrusor pressure at maximum flow rate; PRP: platelet-rich plasma; PVR: postvoid residual; Vol: voided volume; GRA: Global Response Assessment; VAS of SUI: stress urinary incontinence severity by visual analog scale
§ Eights patients in the pretreatment stress test and eleven patients in the posttreatment stress test during the videourodynamic study demonstrated no urinary leakage; the ALPP values of these patients were not included
Table 2. Changes of urinary incontinence severity after PRP injection treatment
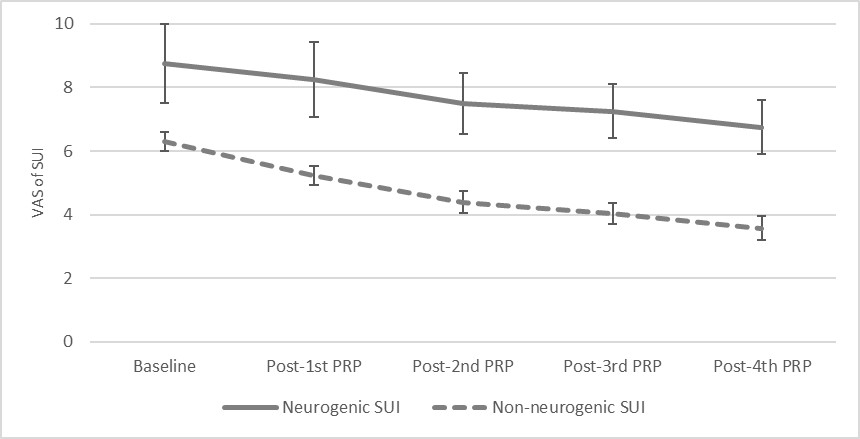
|
|
VAS at baseline
|
VAS after the 1st treatment
|
VAS after the 2nd treatment
|
VAS after the 3rd treatment
|
VAS after the 4th treatment
|
|
Neurogenic SUI
|
8.8±2.5
|
8.3±2.4
|
7.5±1.9
|
7.3±1.7
|
6.8±1.7
|
|
Non-neurogenic SUI
|
6.3±1.7
|
5.3±1.7*
|
4.4±2.0*
|
4.0±1.9*
|
3.6±2.0*
|
|
Total
|
6.6±1.9
|
5.6±2.0*
|
4.7±2.2*
|
4.4±2.1*
|
3.9±2.2*
|
*: p-value < 0.05 compared with baseline data
附件: