個案報告:以頻尿表現之無功能性膀胱副神經節瘤
陳柏翰1、張珝1
1台灣基督長老教會馬偕醫療財團法人馬偕紀念醫院 泌尿科
A case report: Non-functional bladder paraganglioma with urinary frequency
Bo-Han Chen1, Syu Jhang1
Department of Urology, MacKay Memorial Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan1
Background
Bladder paragangliomas account for less than 0.05% of all bladder tumors and less than 1% of all pheochromocytomas, however, the bladder remains the most commonly affected site in the genitourinary tract.[1] Most of the bladder paraganglioma symptoms are related to the over secretion of catecholamine or the mass effect of the tumor. Frequency and urgency of urination, intermittent painless whole course gross hematuria and lumbar discomfort are some of the common symptoms.[2] Preoperative lab data may help to distinguished functional tumor but not non-functional tumor. Image study may show a mass lesion in bladder. Since the above mentioned symptoms are not easily to be diagnosed merely by lab data, image study or physical examination, the precise diagnosis can be made by surgical resection of the tumor. Here, we share a case with finally definite diagnosis of bladder paraganglioma with urinary frequency symptom.
Case presentation
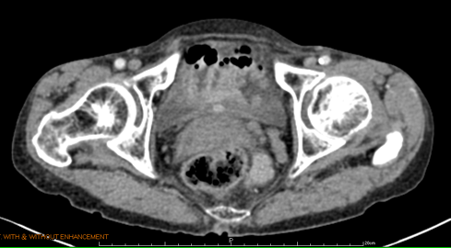
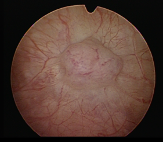
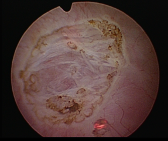
An 81-year-old woman came to our outpatient clinic with the chief complaint of urinary frequency and nocturia for several months. She had underlying disease of bronchiectasis, hypertension, and coronary artery disease. She denied dysuria, lower abdominal or bilateral flank painfulness, smelly urine and gross hematuria. Most of physically examinations were normal. Urine analysis showed numerous red blood cells and 5 white blood cells under high power field. Suprapubic echogram showed bladder distention and a mass lesion at posterior wall. Occasional atypical cells were seen in 2 of 3 sets from voided urine cytology. Computed tomography (CT) scan showed a midline 0.7cm enhancing nodule in posterior wall of urinary bladder. (Figure 1) Further fiberocystoscopic examination revealed a smooth, well-vascularized mass on the posterior wall of the bladder. Differential list included paraganglioma, neurogenic tumor, bladder polyp and other bladder malignancy. Under the impression of bladder tumor, she was admitted for Thulium laser trans-urethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT). (Figure 2)
Visibly complete resection of bladder tumor was done. Postoperative care was smooth without complication. The patient was discharged from hospital the day after operation under stable condition. Pathologic section showed a piece of urinary bladder tissue measuring 0.8 cm in greatest dimension. Microscopically, the section revealed a well circumscribed tumor composed of polygonal cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, arranged in nested pattern. Rich vascular network was present. The tumor cells showed INSM-1(+), synaptophysin(+), chromogranin A(+), GATA-3(focal+), and CK(AE1/AE3)(-). The above mentioned features were compatible with paraganglioma. Outpatient clinic follow-up did not show recurrence one months after surgery.
Discussion and conclusion
Paraganglioma is an extra site of pheochromocytoma.[3] Nonfunctional bladder paragangliomas are occasionally found on imaging studies with the symptoms of urinary discomfort or painless hematuria.[2] In our case the patient suffered from urinary frequency and nocturia. Her bladder tumor was found coincidentally during symptom survey. Most of the extra-adrenal paraganglioma have low malignant potential. However, some of them have a malignant pattern such as local recurrence and pelvis metastasis.[4] As result, surgical resection is the principle treatment for paraganglioma. It is also critical to closely follow up the patient to achieve a better prognosis.
|
Figure 1 CT image showed a midline 0.7cm enhancing nodule in posterior wall of urinary bladder. (arrow) |
|
Figure 2 The tumor was resected by Thulium laser completely. |
 .
. 
1. Zhu X, Zhou M, Yu H, Kuang Y, Chen Y, Li H, Gou X: Bladder paraganglioma managed with transurethral holmium laser resection: A case report. Medicine 2021, 100(34):e26909.
2. Tu X, Zhang N, Zhuang X, Chen S, Luo X: Incidental diagnosis of nonfunctional bladder paraganglioma: a case report and literature review. BMC Urology 2021, 21(1):98.
3. Iwamoto G, Kawahara T, Tanabe M, Ninomiya S, Takamoto D, Mochizuki T, Kuroda S, Takeshima T, Izumi K, Hattori Y et al: Paraganglioma in the bladder: a case report. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2017, 11(1):306.
4. Yoo KH, Choi T, Lee H-L, Song MJ, Chung BI: Aggressive Paraganglioma of the Urinary Bladder with Local Recurrence and Pelvic Metastasis. Pathology & Oncology Research 2020, 26(4):2827-2829.