高尿草酸老鼠餵食過度限鈉的飲食反而增加草酸鈣腎結石風險
黃鶴翔、劉展榮1
成大醫院泌尿部1
Restricted dietary sodium intake in hyperoxaluric rats increases the risk of calcium oxalate nephrolithiasis
Ho-Shiang Huang, Chan-Jung Liu1
Department of Urology, National Cheng Kung University Hospital, Tainan, Taiwan
Purpose: This study aims to investigate the changes in the abundance of renal aquaporins and major sodium transporters after dietary sodium restriction in hyperoxaluria rats, and their influence on renal calcium oxalate (CaOx) stone formation.
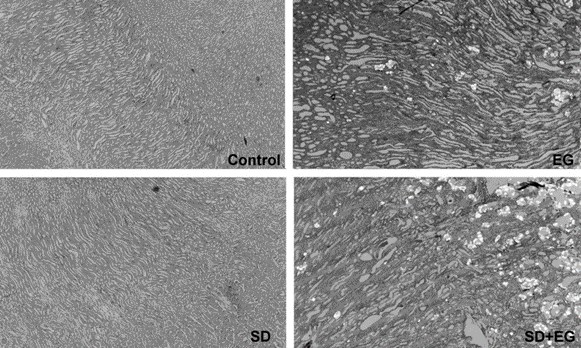
Materials and Methods: There were four groups in this study, eight control rats received 50 meq/L NaCl in drinking water and sodium deficient (SD) diet, eight EG rats received 50 meq/L NaCl +0.75% ethylene glycol (EG) in drinking water +SD diet, eight SD rats received SD diet + drinking water (No NaCl), and eight SD+EG rats received SD diet+0.75% EG + drinking water. The expression of renal aquaporins and major sodium transporters were examined by Western blots. Urinary biochemistry, renal functional parameters, urinary CaOx relative supersaturation, and CaOx crystal accumulation were evaluated.
Results: In EG rats, the abundance of renal major sodium transporters remained unchanged, whereas renal aquaporin-1 (AQP1), AQP2 and AQP3 abundances decreased significantly when compared with the controls. In SD+EG rats, the abundance of renal type 3 Na/H exchanger, thiazide-sensitive Na-Cl cotransporter, Na-K-ATPase, and AQP1 markedly reduced, consistent with reduced urine osmolality and increased fractional excretion of Na and rate of urinary Na excretion when compared with SD rats. Increased AP(CaOx)index, urinary Ca/Cr ratio, urinary lipid peroxides, tubular enzymuria, and renal CaOx score were also noted in SD+EG rats.
Conclusions: Long-term dietary sodium restriction to EG rats will increase urinary Na and water loss and the associated hypercalciuria and impaired renal function may further predispose the hyperoxaluric kidney to massive CaOx crystal accumulation.