臨床尿胸案例分享
劉瑞文、何承勳
衛生福利部立雙和醫院 泌尿科
Case sharing of urinothorax
Liu Jui Wen, Ho Cheng Hsun
Department of Urology, Shuang Ho hospital, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan
Introduction: Urinothorax is rare condition about transudate of pleural effusion. We are sharing one urinothroax case evaluation and management.
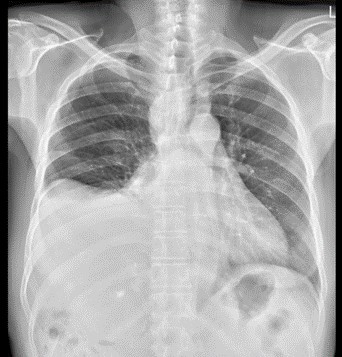
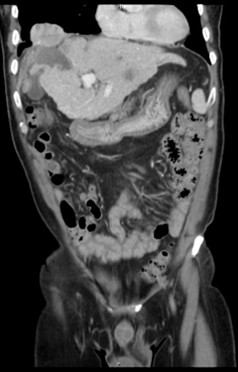
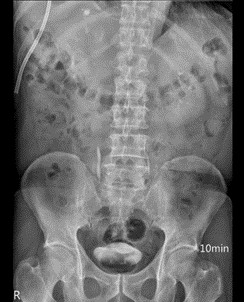
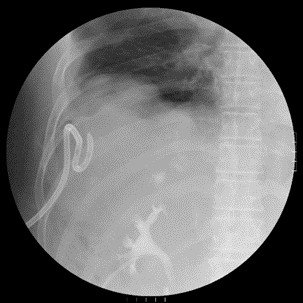
Case report: This 61 years old male patient has past history of hepatitis C virus infection, hepatocellular carcinoma status posts several time radiofrequency ablation and transcatheter arterial embolism, esophageal varices status post endoscopic ligation. This time he was suffered from cough and easily short of breath for 1 week. So he was transferred to chest out-patient department from gastrointestinal department. Chest X ray showed progressive right pleural effusion. Pigtail insertion under sonography was done and urine like fluid was drained. Pleural effusion test showed 0.72 and 0.74 in serum. So urinothorax was diagnosed according to definition. IVP was done and showed obvious contrast leakage to pleural space. Right lower lung tumor was undergone CT guide biopsy and pathological report showed poorly-differentiated carcinoma which may be compatible metastatic HCC. Ureteroscopy examination, ureteral catheter insertion and percutaneous nephrostomy drain were done and no obvious ureteral defect was found. Antegrade pyelography showed still no contrast leakage. Pleural effusion amount was decreasing after ureteral catheter insertion. Then we shifted catheter to double J catheter. His clinical presentation was stable after that.
 |
 |
|
Initial pleural effusion
|
Right lower lung tumor
|
 |
 |
|
IVP showed no contrast leakage
|
AP from PCND showed no contrast leakage
|
Discussion: Definition of urinothorax is pleural fluid creatinine to serum ratio >1 and diagnostic if >1.7. It is extremely rare condition of pleural effusion. Fluid is arriving pleural space through retroperitoneal spcae under the posterior diaphragm, or via the retro peritoneal lymphatics. Cause is obstruction due to trauma or iatrogenic. Clinical symptom is respiratory system influence, chest pain, reduce urine. Drainage of urinothorax smell as ammonia and diagnosed with acidity, low glucose level, high LDH, low total protein. Treatment is obstruction management and some cases will resolve on their own. Back to our patient, he accepted RFA due to HCC and lung malignant metastasis. We suspect that cause of urinothorax is urinary tract micro-perforation or lymphatic spread. After intra-renal pressure releasing and fully evaluation, his clinical presentation is improving gradually.
附件: