嗜酸性粒細胞性膀胱炎以膀胱腫瘤表現之罕見案例報告
廖偉創1、賴昱維2、薛又仁2、黃建榮2、蕭毅君2、邱文祥2
1臺北市立聯合醫院忠孝院區外科部泌尿科
2臺北市立聯合醫院仁愛院區外科部泌尿科
Eosinophilic cystitis presenting as bulging bladder mass: a case report of rare disease
Wei-Chuang Liao1, Yu-Wei Lai2, Thomas Y. Hsueh2, Andy C. Huang2, Yi-Chun Hsiao2, Allen W. Chiu2
1Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, Taipei City Hospital, Zhongxiao Branch
2Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, Taipei City Hospital, Renai Branch
Introduction
Eosinophilic cystitis (EC) is a rare inflammatory bladder disease which occurs in all age groups. Patients often present with urinary frequency, hematuria, urgency, retention, dysuria and suprapubic pain. The common clinical manifestations were presence of bladder mass, thickened bladder wall and peripheral eosinophilia. We describe a case of EC in 39-year-old man presenting with lower urinary symptoms and bladder mass.
Case presentation
A 39-year-old man with a medical history of allergic rhinitis, went to our urologic clinic due to dysuria, frequency and urgency throughout 2 weeks. Urinalysis showed microscopic hematuria and proteinuria. Blood test showed peripheral eosinophilia with eosinophil measured 25% and count 1220 per microliter of blood. The kidney ultrasound demonstrated bilateral tiny renal calcifications without hydronephrosis. Urine cytology showed no evidence of malignancy with presence of few bland-looking urothelial cells. The intravenous pyelography reported irregular urinary bladder wall with filling defect (Fig. 1). Cystoscopy revealed a bulging mass with erythematous surface under the dome of urinary bladder (Fig. 2). The patient underwent TUR surgery (Fig. 2) and the specimen was obtained. The histological findings showed cystitis with mucosal erosion, numerous eosinophils and few lymphoplasma cells infiltration. The pathological diagnosis was EC. The patient’s symptoms resolved after operation and he had no recurrence of symptoms during 3-month follow-up. Subsequent urinalysis showed normal findings.
Conclusion
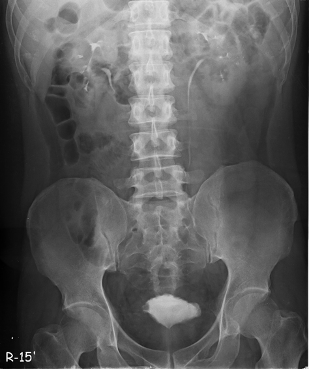
Fig. 1 Intravenous pyelography (IVP) showed irregular contour
of urinary bladder with filling defect.
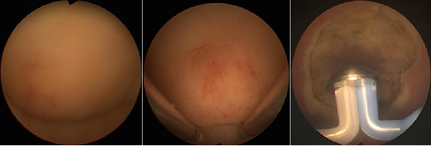
Fig. 2 Cystoscopy showed a bulging mass under the dome of urinary bladder. The lesion
after hemostatic transurethral resection (TUR).